The lightning strike is both one of the most fascinating and dangerous metrological phenomenon. Mankind as always been attracted to the phenomenon that they thought was a form of divine power : it is the weapon of Zeus, the king of the gods of the Olympus and it is the power of Thor. But beyond these belief lies the fear of a dangerous phenomenon that man needs to contain for its own safety. Lightning can be a major issue particularly when talking about tall buildings. That is why lightning protection is so important.
Lightning Protection
A lightning protection system is designed to protect a structure from damage due to lightning strikes by intercepting such strikes and safely passing their extremely high currents to ground. A lightning protection system includes a network of air terminals, bonding conductors, and ground electrodes designed to provide a low impedance path to ground for potential strikes. Different solutions are currently available to the world. ILPA strongly believes in the most simple, efficient and modern device used to protect people and buildings from lightning strikes : the Early Streamer Emission (ESE) lightning conductor.
Early Streamer Emission
If a lightning rod has a mechanism producing ionization near its tip, then its lightning capture area is greatly increased. At first, small quantities of radioactive isotopes were used as sources of ionization between 1930 and 1980, later replaced with various electrical and electronic devices. According to an early patent. Since most lightning protectors’ ground potentials are elevated, the path distance from the source to the elevated ground point will be shorter, creating a stronger field (measured in volts per unit distance) and that structure will be more prone to ionization and breakdown. You can find out more about the specifications of various ESE in our technical papers section.
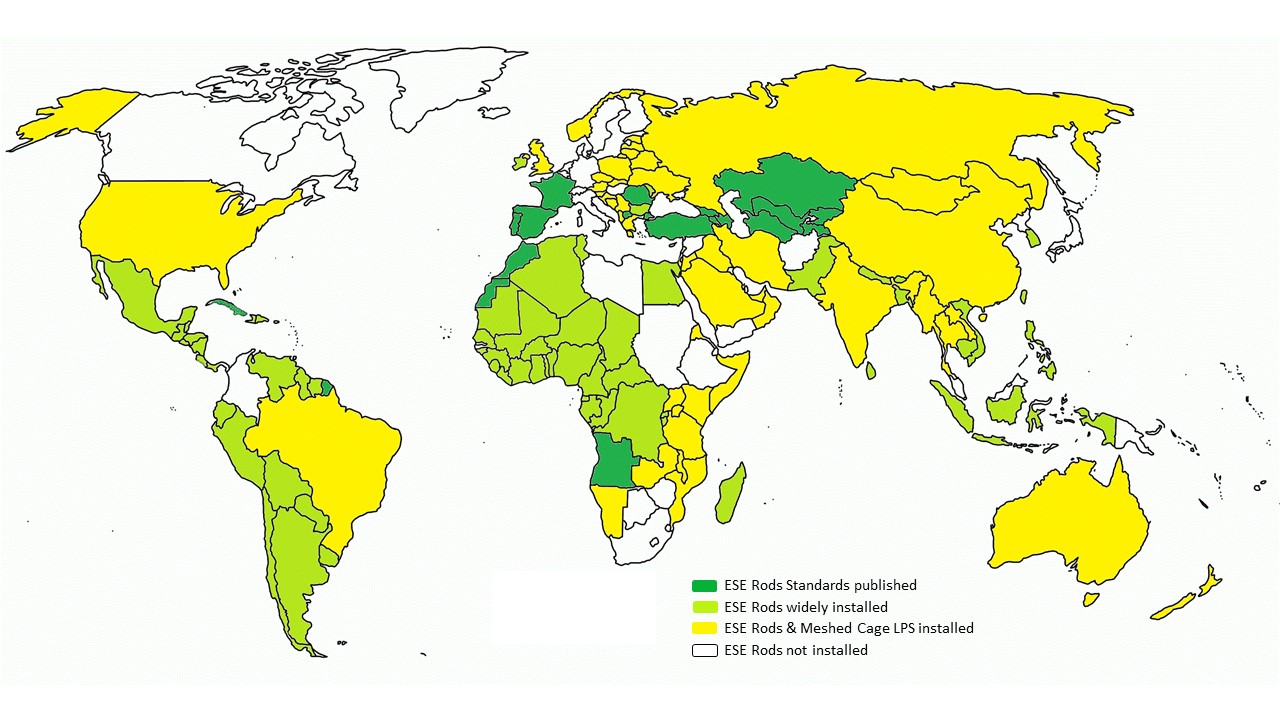
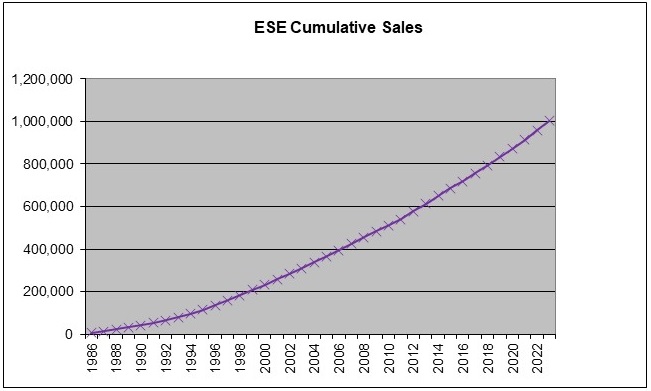
Today, ESEs are widely used in different parts of the globe (see map below). In 1986, which is the first year of available statistics, number of ESE was 4 088 when in 1996 it was already a cumulated number of 112 412 units. It reached the million mark (1,00,350 exactly for European manufacturers) in 2023! The last 35 years have shown that ESE air-terminals are efficient and that the ESE solution is a reliable solution for lightning protection.